
Merely placing an order for goods is not a recordable transaction because no exchange has taken place. In the coming sections, you will learn more about the different kinds of financial statements accountants generate for businesses. The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. Through these examples, you can see how every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, always keeping the accounting equation in balance. This simple equation forms the foundation of double-entry bookkeeping, ensuring every debit has a corresponding credit. The accounting equation, whether in its basic form or its expanded version, shows the relationship between the left side (assets) and the right side (liabilities plus capital).
The accounting equation formula is: Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ or Stockholders’ Equity.
One of the main benefits of using the accounting equation is the fact that it provides an easy way to verify the accuracy of your bookkeeping. Are your liabilities significantly higher than your assets? This may indicate that you aren’t managing your money very well. On the other hand, if the equation balances, it is a good indication that your finances are on the right track. We saw above that owner’s equity only relates to investments made personally by the owner. In this example, we used the business bank account to purchase a business asset.
Un hecho interesante sobre la salud masculina es que factores como el estrés, la ansiedad y ciertas condiciones médicas pueden contribuir a la disfunción eréctil. Muchos hombres, al enfrentar este problema, buscan soluciones que pueden incluir tratamientos médicos. Por ejemplo, algunos optan por alternativas como el medicamento para afecciones urinarias que se puede obtener sin receta, lo que les lleva a considerar opciones para ***. Es importante recordar que, aunque algunos medicamentos pueden ayudar, siempre es recomendable consultar a un médico para obtener un diagnóstico adecuado y un tratamiento eficaz.
- This arrangement is used to highlight the creditors instead of the owners.
- Liabilities are owed to third parties, whereas Equity is owed to the owners of the business.
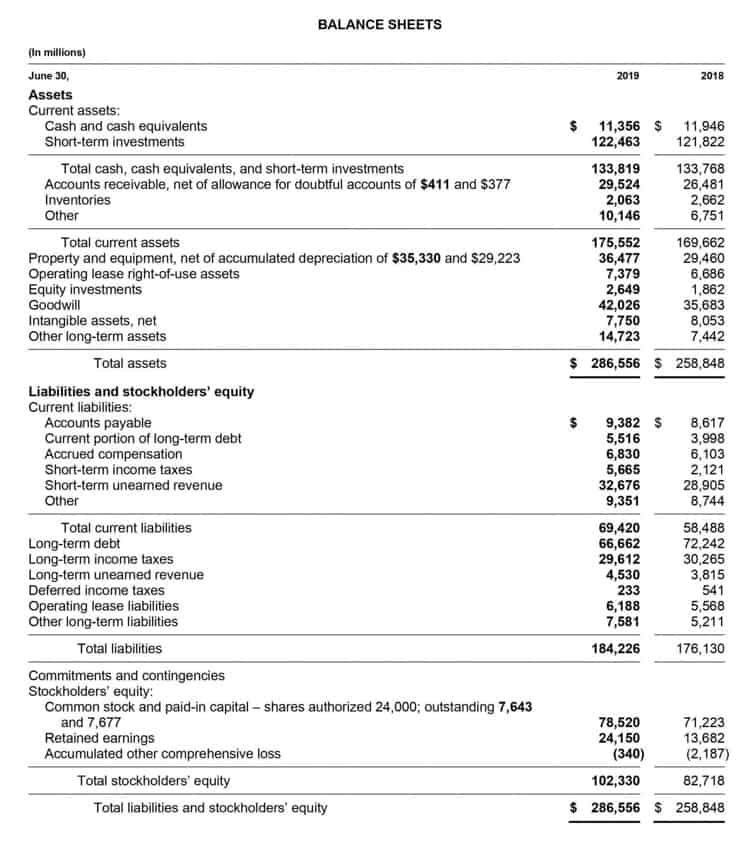
- As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets.
- The OCF portion of the equation can be broken down and be calculated separately by subtracting the any taxes due and change in net working capital from EBITDA.
Arrangement #1: Equity = Assets – Liabilities
Additionally, you can use your cover letter to detail other experiences you have with the accounting equation. For example, you can talk about a time you balanced the books for a friend or family member’s small business. This transaction affects only the assets of the equation; therefore there is no corresponding effect in liabilities or shareholder’s equity on the right side of the equation. For every transaction, both sides of this equation must have an equal net effect. Below are some examples of transactions and how they affect the accounting equation. It’s important to note that excess cash does not always mean the company is doing well or what it should be doing to grow in the future.
Un aspecto interesante sobre la salud masculina es que muchos hombres experimentan problemas relacionados con la función sexual a lo largo de sus vidas. De hecho, se estima que una de cada cuatro personas que buscan tratamiento para esta condición son menores de 40 años. Aunque existen diversas causas para estos problemas, desde factores psicológicos hasta afecciones médicas, la conversación abierta sobre el tema es esencial para el bienestar. Algunos hombres pueden buscar tratamientos como el medicamento que se puede obtener al “, aunque es importante consultar a un médico antes de tomar cualquier decisión. La educación y el apoyo son fundamentales para abordar este tema común y sensible.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Statement Modeling
Liabilities are owed to third parties, whereas Equity is owed to the owners of the business. Paul Boyce is an economics editor with over 10 years experience in the industry. Currently working as a consultant within the financial services sector, Paul is the CEO and chief editor of BoyceWire.
While single-entry accounting can help you kickstart your bookkeeping knowledge, it’s a dated process that many other business owners, investors, and banks won’t rely on. That’s why you’re better off starting with double-entry bookkeeping, even if you don’t do much reporting beyond a standard profit and loss statement. If a business buys raw materials and pays in cash, it will result in an increase in the company’s inventory (an asset) while reducing cash capital (another asset).
It provides the foundation for the rules of debit and credit in the journalizing process, where for each transaction total debits must equal total credits. As a result, theaccounting equation must be in balance at all times for a business’ financial records to be correct. It involves the three types of accounts that do not appear on the income statement.
- Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity represent how the assets of a company are financed.
- Revenue and expense accounts were used temporarily and were ultimately closed to Retained Earnings.
- It adjusts the month’s beginning retained earnings balance by adding net income from the income statement and subtracting out dividends declared.
- Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
- Liabilities are anything that the company owes to external parties, such as lenders and suppliers.
- For example, ABC Co. started the company on 02 January 2020 by injecting cash into the business of $50,000.

It helps to prepare a balance sheet, so it is also called the Balance Sheet Equation. Record each of the above transactions on your balance sheet. Add the $10,000 startup equity from the first example to the $500 sales equity in example three. Add the accounting equation broken down total equity to the $2,000 liabilities from example two. These elements are basically capital and retained earnings; however, the expanded accounting equation is usually broken down further by replacing the retained earnings part with its elements.
Ready to grow your business?
Understanding how to use the formula is a crucial skill for accountants because it’s a quick way to check the accuracy of transaction records . Now that you are familiar with some basic concepts of the accounting equation and balance sheet let’s explore some practice examples you can try for yourself. This equation sets the foundation of double-entry accounting, also known as double-entry bookkeeping, and highlights the structure of the balance sheet. Double-entry accounting is a system where every transaction affects at least two accounts. The accounting equation stems from the double-entry bookkeeping system, a principle that mandates every financial transaction impact at least two accounts to maintain a balanced equation. The accounting equation ensures that the company’s accounts are always in balance and that a company’s financial reports are always accurate.

- This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system.
- The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced.
- Any investment of personal assets will increase your owner’s equity.
- Investors are interested in a business’s cash flow compared to its liability, which reflects current debts and bills.
- The remainder of the liquidated assets will be used to pay off parts of shareholder’s equity until no funds are remaining.
- Stockholders can transfer their ownership of shares to any other investor at any time.
Due to this, the accounting equation is also called the balance sheet equation sometimes. In terms of results, in double-entry accounting both sides of the accounting equation are required to balance out at all times. For example, if your business assets total $200,000, the sum of your liabilities plus the owners’ or stockholders’ equity also equals $200,000.

